How Glass Bottles Are Produced
Glass bottles are produced through a process called glassblowing or glass molding. The process involves heating glass to a high temperature until it becomes molten. The molten glass is then shaped using various techniques, such as blowing air into a mold or using a glassblower’s tools to shape it manually.
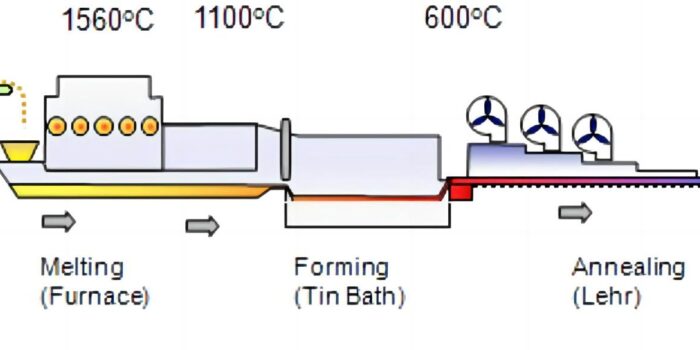
First, raw materials like silica sand, soda ash, and limestone are mixed together and melted in a furnace at around 1500 degrees Celsius. This mixture forms molten glass. The molten glass is then fed into a machine called an IS machine, which shapes the glass into bottles.
In the IS machine, the molten glass is guided into a mold, where it is blown into shape using compressed air. The mold gives the glass its desired shape, such as a bottle. The glass is then cooled rapidly to harden it and prevent deformation.
After the bottles are formed, they go through a process called annealing, where they are slowly cooled to relieve internal stresses and increase their strength. This helps to prevent the bottles from breaking easily.
Once the bottles have been annealed, they can be further processed, such as being decorated with labels or designs, and then packaged for distribution.
Overall, the production of glass bottles involves a combination of high-temperature melting, shaping, cooling, and annealing processes to create the final product.




This Post Has 0 Comments